Consider you are coming home from a long hectic day at work, and just by saying a few words, the lights get softer, your favorite music begins to play, and the room temperature feels just right. This smooth and easy setup is what a smart home offers, and it all works thanks to Wi-Fi. But is Wi-Fi for smart homes the ultimate solution, or does it come with hidden pitfalls?
In this deep dive, we’ll explore the strengths and weaknesses of using Wi-Fi to connect your smart devices, drawing on current trends like Wi-Fi 7 and AI integration. Whether you’re getting your first smart bulb or growing your whole smart home setup, knowing these things can help you create a stronger and safer home network.
As we move into 2025, the smart home industry is growing fast, with estimates showing more than 500 million smart home devices in U.S.
Even though there are so many devices available, Wi-Fi remains the primary method people use to connect. It’s simple to use, but it’s still important to ensure it functions properly. Let’s take a closer look.
What Is Wi-Fi for Smart Homes?
At its core, Wi-Fi for smart homes refers to the wireless network that links devices like smart thermostats, security cameras, and voice assistants to the internet and each other. Unlike wired alternatives such as Ethernet or specialized protocols like Zigbee, Wi-Fi uses radio waves to transmit data, allowing for easy setup without drilling holes or running cables.
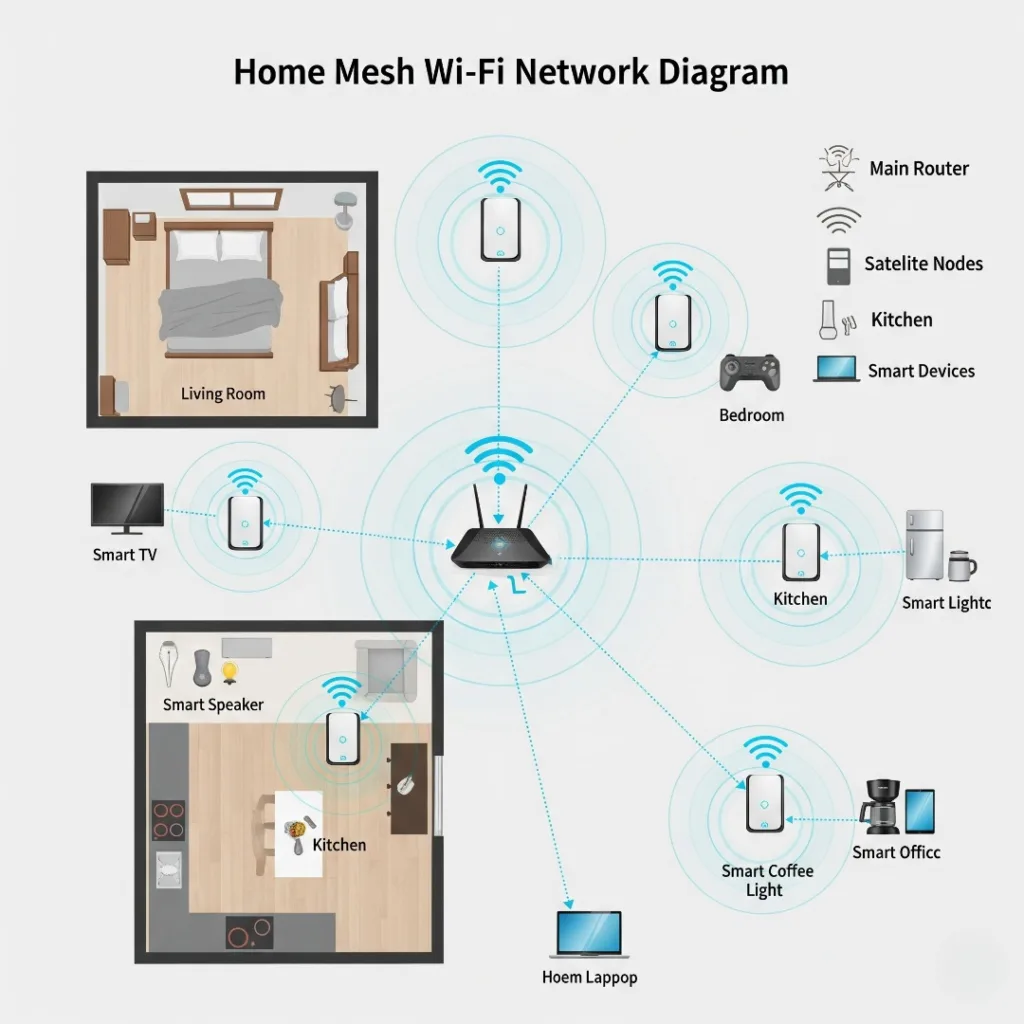
In a typical setup, your router acts as the central hub, broadcasting signals that devices connect to. With advancements like mesh systems—networks of multiple nodes that extend coverage—smart home Wi-Fi can blanket even large homes. For example, a family in a two-story house might use a mesh router to ensure their outdoor security camera stays connected without dropouts.
But why choose Wi-Fi over other options? It boils down to accessibility. Most homes already have a router, making it a low-barrier entry point for automation.
Strengths of Wi-Fi in Smart Homes
Wi-Fi performs well in multiple areas, which is why it’s a popular choice for today’s home users. Let’s take a closer look at its main benefits.
Seamless Connectivity and Scalability
One of the biggest strengths of Wi-Fi for smart homes is its ability to handle dozens of devices simultaneously. With Wi-Fi 6 and the emerging Wi-Fi 7, networks can support up to 9.6 Gbps speeds—nearly three times faster than older standards—thanks to technologies like OFDMA and MU-MIMO. This means your smart fridge can update recipes while your robot vacuum navigates the living room, all without lag.
Take scalability: As you add more gadgets, Wi-Fi adapts easily. A real-life example? A tech-savvy couple starts with smart lights in the kitchen, then expands to voice-controlled blinds and a home theater system. Mesh networks eliminate dead zones, ensuring consistent performance across the house.
AI integration is becoming a growing trend in 2025. Devices now use Wi-Fi to leverage cloud-based AI for predictive automation, like adjusting lights based on your routine.
High Bandwidth for Demanding Tasks
For homes with streaming needs, Wi-Fi excels in bandwidth. It supports high-data activities like 4K video from security cams or audio streaming from smart speakers. Compared to low-bandwidth protocols like Z-Wave, Wi-Fi handles it all in one network.
Picture this: During a family movie night, your smart TV streams in ultra-HD while the kids’ tablets run games, and the oven preheats via app—all on the same Wi-Fi connection. This versatility is why it’s ideal for multimedia-heavy smart homes.
Ease of Setup and Flexibility
No one likes a complicated setup. You don’t need extra hubs for most of Wi-Fi devices which can connect quickly through a simple app scan. This makes it easy to move devices around without having to rewire, which is great for renters or people experimenting with smart home automation.
The Matter protocol is making these trends even better by allowing devices from different brands to work together over Wi-Fi.
This lowers the risk of being locked into one brand’s system. By 2025, your Google Nest thermostat would be able to work well with an Amazon Echo without any issues.
Weaknesses of Wi-Fi in Smart Homes
Despite its perks, Wi-Fi isn’t flawless. Several drawbacks can frustrate users, especially in larger or device-dense setups.
Security Vulnerabilities
Security is a big problem. Smart home Wi-Fi devices are commonly targeted by hackers, leading to issues like someone getting into your cameras or personal data being stolen. Since these devices use wireless signals, they can be easier to hack compared to wired systems. Additionally, many low-cost devices don’t have strong encryption to protect your information.
There was an incident in 2024 where hackers used weak Wi-Fi passwords to take control of smart locks.
It’s important for homeowners to use WPA3 encryption and keep their devices updated regularly as the number of attacks on IoT devices has gone up by 30% each year.
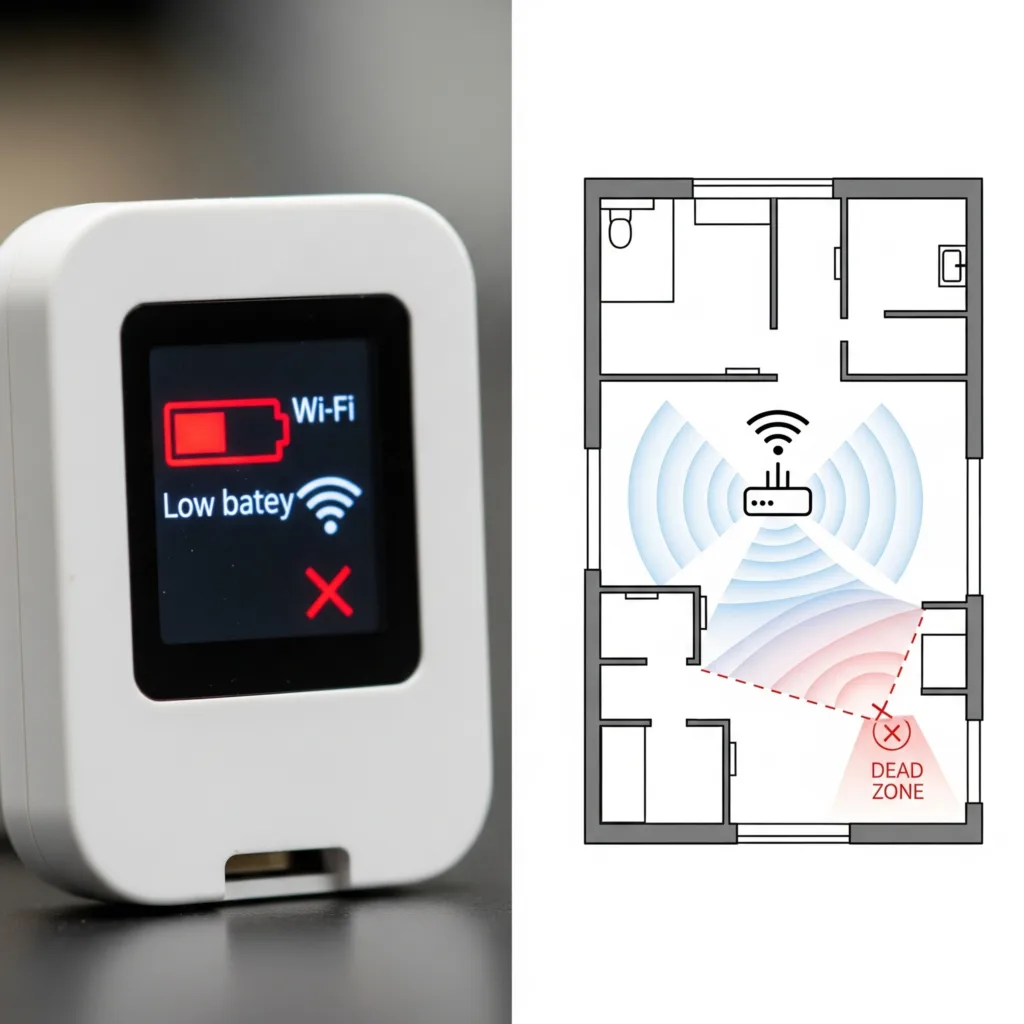
Interference and Range Limitations
Wi-Fi signals can suffer from interference from microwaves, walls, or neighboring networks, leading to dropouts. In big homes, range is an issue—standard routers might not reach the backyard.
Compare this to Zigbee, which uses mesh topology for better reliability in low-power scenarios. A common complaint: Your garage door opener works fine near the router but fails upstairs due to signal weakness.
High Power Consumption and Bandwidth Contention
Wi-Fi uses a lot of power, which quickly drains the battery in devices like sensors. This is different from more energy-saving options like Bluetooth LE. Also, smart devices take up bandwidth that could be used by laptops and phones, leading to slower performance. In a household with 50+ devices—a 2025 norm—this can lead to frustration during peak times.
Energy trends are addressing this, with AI optimizing power use, but it’s still a hurdle.
Current Trends and Innovations in Smart Home Wi-Fi
Looking ahead to 2025, Wi-Fi for smart homes is evolving rapidly. Wi-Fi 7 promises ultra-low latency and better multi-device handling, ideal for AR/VR integrations in homes.
AI is embedding deeper, with routers using machine learning to predict and prevent outages. Sustainability is key too—energy-saving modes reduce consumption amid rising eco-concerns.
Multi-protocol hubs are rising, blending Wi-Fi with Zigbee for hybrid strengths. For fresh insight: As 5G home internet grows, it complements Wi-Fi for redundancy, but Wi-Fi 6E/7 edges out for indoor density.
For more on Wi-Fi standards, visit the IEEE website.
Tips for Optimizing Wi-Fi in Your Smart Home
To maximize strengths and minimize weaknesses:
- Invest in a Wi-Fi 6 or 7 mesh router for coverage.
- Use guest networks for IoT devices to isolate risks.
- Position routers centrally and avoid metal obstructions.
- Regularly update firmware to patch vulnerabilities.
For more technical content, consider our guide on “Internet connectivity requirements for home automation“
A pro tip: Test your setup with tools like speed tests—aim for at least 100 Mbps for smooth automation.
FAQ: Common Questions on Wi-Fi for Smart Homes
What are the main advantages of using Wi-Fi 6 for smart homes?
Wi-Fi 6 offers better efficiency for multiple devices, reducing lag in automation scenarios like voice commands. It’s great for homes with 20+ gadgets.
How do security risks in smart home Wi-Fi compare to wired systems?
Wireless setups face more interception risks, but with strong passwords and encryption, they’re comparable. Wired options like Ethernet are inherently safer but less flexible.
Is Wi-Fi reliable enough for critical smart home functions like security?
Yes, with mesh systems and backups, but interference can be an issue. For reliability, a hybrid with Zigbee for alarms is recommended.
What long-term costs come with Wi-Fi-dependent smart homes?
Beyond router upgrades, factor in higher electricity costs from power-hungry devices and potential subscription fees for cloud services.
How does Wi-Fi 7 improve weaknesses in smart home networks?
It boosts speeds and reduces contention, making it ideal for AI-driven homes with many sensors.
Conclusion: Balancing the Scales for Your Smart Home
In summary, Wi-Fi for smart homes offers unmatched convenience, scalability, and bandwidth, but it grapples with security, interference, and power issues. By using 2025 trends such as Wi-Fi 7 and AI improvements, you can make the most of your strengths. Whether you’re setting up automation for better efficiency or for enjoyment, a properly designed Wi-Fi system can greatly improve everyday life—make sure it’s both secure and reliable.
Ready to enhance your home? Start by auditing your current network and consider an upgrade. For more tips, explore our blog on Smart Home Devices and Systems.


