The smart home automation industry is absolutely exploding right now, and when you see the numbers, experts predict that the global market will reach about $1.4 trillion by 2034, which is incredible.
If you’re considering diving into smart homes – and really, who isn’t these days? – One of the first big choices you’ll need to make is whether to go with a centralized or decentralized home automation system.
- Understanding Home Automation System Architectures
- Centralized Home Automation: Advantages and Disadvantages
- Decentralized Home Automation:
- Comparative Analysis:
- Industry Trends and Future Outlook
- Choosing the Right System as per requirements
- Implementation Best Practices
- Conclusion: The Future of Home Automation
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
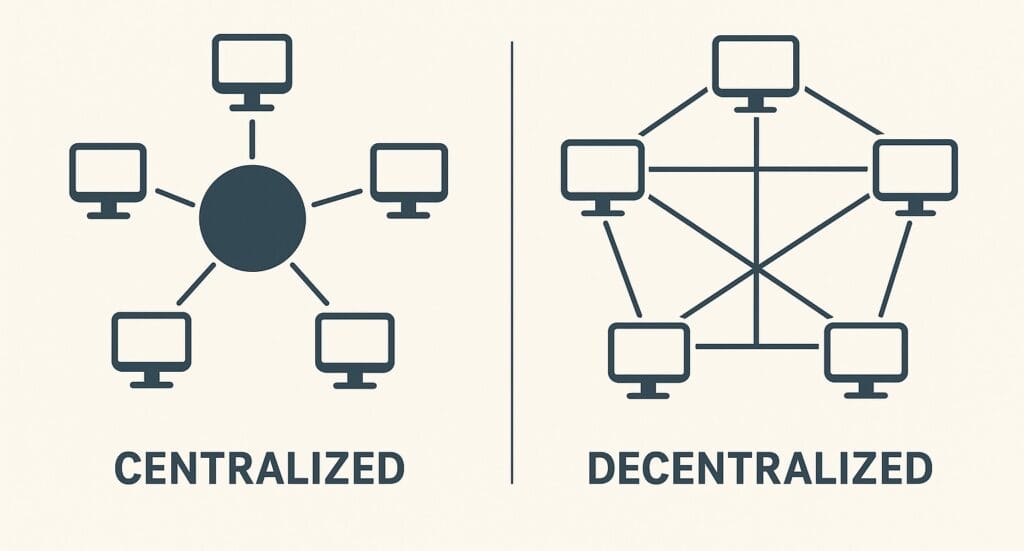
Understanding Home Automation System Architectures
When planning your smart home integration, understanding the fundamental differences between centralized and decentralized approaches is essential. Both methods have their own pros and cons that affect how well your home works, how reliable it is, and whether you can easily expand it down the road.
What is Centralized Home Automation?
A centralized home automation system operates through a single, powerful control hub that manages all connected devices and smart home protocols. Think of it as your smart home’s brain – everything from your devices and sensors to all your automation rules runs through this one central hub.
Key characteristics of centralized systems include:
- Single point of control and management
- All devices communicate through the central hub
- Unified interface for system monitoring and control
- Centralized data processing and storage
- Traditional wired infrastructure requirements
Popular centralized systems include Control4, Crestron, and Savant systems, which have dominated the luxury home automation market for years.
What is Decentralized Home Automation?
In contrast, a decentralized home automation system distributes intelligence across multiple devices that communicate directly with each other. Instead of depending on one central hub, your devices create a mesh network where each piece can work on its own while still talking to the others.
Defining features of decentralized systems:
- Distributed processing across multiple devices
- Device-to-device communication protocols
- Multiple points of control and redundancy
- Wireless mesh networking capabilities
- Modular and scalable architecture
Well-known platforms such as Zigbee, Z-Wave, and Matter are great examples of decentralized systems.
Centralized Home Automation: Advantages and Disadvantages
Benefits of Centralized Systems
1. Simplified Management and Control
Centralized systems really shine when it comes to keeping everything simple and unified. Getting your devices up and running is quick, and tweaking things afterward is a breeze. Homeowners absolutely love having one central spot to control their lights, security, climate, and entertainment – no jumping between different apps or interfaces.
2. Robust Performance and Processing Power
Central hubs usually pack some serious processing power that can handle complex automation and make decisions in real-time. What this means for you is quicker response times and way more advanced smart home setups.
3. Professional Installation and Support
Most centralized systems deliver top performance and come with full professional installation, along with ongoing tech support whenever you run into problems.
4. Advanced Integration Capabilities
Centralized platforms often offer superior integration with high-end audio-visual equipment, security systems, and building management technologies.

Drawbacks of Centralized Systems
1. Single Point of Failure Risk
When your controller fails, everything in your system stops working. That’s really the biggest weakness of centralized setups – one broken hub means your entire smart home goes dark..
2. Higher Initial Investment
If your controller goes down, your whole system crashes with it. The largest drawback of a centralized system is that a malfunction in the main controller might put your entire smart home to a complete stop.
3. Limited Scalability and Flexibility
Generally speaking, a centralized system’s expansion requires expert help and can be expensive. Adding new devices or changing the arrangement might require considerable rewiring or major hardware changes.
4. Concerns about relying on a single vendor
Some manufacturers use specific protocols and hardware which can limit your options of system upgrades or flexibility.
Decentralized Home Automation:
Benefits of Decentralized Systems
1. Enhanced Reliability and Resilience
Decentralized systems provide unparalleled resilience, longevity, and the assurance that your smart home will continue to function seamlessly even in the face of unforeseen device failures. If one component fails, the rest of the system continues operating normally.
2. Cost-Effective Implementation
Decentralized systems work with the wiring your home already has, which makes installation simpler and more affordable. You can start small and easily grow your setup as needed.
3. Superior Scalability and Modularity
Adding new devices to decentralized systems is generally simple, involving minimal configuration and no need for rewiring. This makes system expansion both cost-effective and convenient.
4. Freedom from vendors and Device Compatibility
Different brands’ devices can work smoothly with one another using open standards like Matter, Thread, and Zigbee. This prevents vendor lock-in and helps keep your system compatible in the long run.

Drawbacks of Decentralized Systems
1. Network Complexity and Management
When your system gets bigger, keeping track of all the devices and how they talk to each other can become tricky. Often, the problems can be fixed by spotting and correcting faulty modes.
2. Potential Latency and Communication Issues
In big houses or places with much wireless interference, especially when using mesh networks, you might notice the system slowing down at times or devices losing connection briefly.
3. Security Considerations
Decentralized systems need to pay close attention to cybersecurity best practices and update the firmware on all of their components on a regular basis because more devices are acting as possible entry points.
4. Learning Curve and DIY Requirements
With many decentralized systems, you’re expected to handle the setup, configuration, and maintenance yourself. Homeowners with less technical knowledge find it more challenging.
Comparative Analysis:
| Category | Centralized Systems | Decentralized Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Investment | Higher upfront costs | Low initial investment |
| Running Costs | Expert maintenance, complete system updates | Step-by-step item replacement, lower maintenance costs |
| Reliability Assessment | High reliability, total failure risk if the central hub fails. Expert assistance accessible | Distributed failure tolerance. Individual devices do not affect entire system. Self-maintaining mesh network |
Scalability and Future-Proofing
Market trends indicate a strong shift toward decentralized architectures, driven by improved wireless protocols and the emergence of Matter as a universal standard. The global smart home automation market size is expected to increase to USD 1,149 billion by 2034 from USD 104.36 billion in 2024, with much of this growth attributed to accessible, modular solutions.
Industry Trends and Future Outlook
Current Market Dynamics
The home automation business is undergoing a significant transition. Safety and security systems accounted for 44.20% of industry revenue in 2024 which indicated that security remains the primary reason many individuals choose to improve their houses. Home automation is more than simply a luxury; it is also a wise investment. Adding smart devices to your home can actually increase a property’s resale value by roughly 5%.
Emerging Technologies
1. Matter Protocol Revolution
Matter is quickly turning into the common language for smart home devices, making it simple for products from different brands to work together smoothly
2. Edge Computing Integration
Smart IoT devices can process data on their own these days, giving you the benefits of a central “brain” even in a decentralized setup.
3. AI-Powered Automation
Machine learning algorithms that learn from user behavior and environmental conditions are making automation smarter and more adaptive.
Professional vs. DIY Installations
The smart home market is increasingly giving homeowners more control and the chance to customize their setups, developing DIY solutions. It is said especially that more complicated installations still benefit from professional help for:
- Large-scale residential projects
- Integrating with existing building systems
- Custom automation programming
- Installing and configuring security systems
Choosing the Right System as per requirements
Centralized Systems Are Ideal For:
- High-end homes having sophisticated integration
- Professional installation and ongoing support
- Homes with complex audio and video setups
- Smart devices management from a single interface
- New construction projects designed with smart home features
Decentralized Systems Excel When:
- Budget constraints are a primary consideration
- DIY installation is preferred
- Planned Gradual system expansion
- Reliability and redundancy are on priorities
- Interoperability between different brands is important
Implementation Best Practices
For Centralized Systems:
1. Professional Planning Work with certified installers to design optimal system architecture and infrastructure requirements.
2. Infrastructure Investment: Ensure that your home has sufficient electricity, network, and control wiring in place throughout the building or large renovations.
3. Future-Proofing: Choose systems that offer upgrade options and solid manufacturer support.
For Decentralized Systems:
- Strong Network – Ensure strong Wi-Fi coverage everywhere, and a dedicated IoT network for the best performance.
- Protocol Selection – Choose devices that support Matter, Thread, or other forward-looking standards to keep your system compatible with future technology.
- Step by Step Setup – Begin with basic needs like lighting and security, and then expand the scope of your home automation setup one step at a time.
Conclusion: The Future of Home Automation
Choosing between centralized and decentralized home automation really depends on your needs, budget, and long-term goals. Centralized systems are still a good fit for luxury homes with complex needs, but decentralized setups are gaining popularity due to their flexibility, affordability, and reliability.
You need decentralized systems when:
- Cost-effective implementation and expansion
- System reliability and fault tolerance
- Vendor independence and device choice
- DIY installation and management capabilities
You need a centralized system when:
- Professional installation and continuing assistance.
- Centralized control and seamless system integration.
- Compatibility with high-end audiovisual installations
- Advanced programming techniques for automation
Furthermore, hybrid systems that combine centralized processing power with decentralized device communication are emerging, and offering the best practices. With the rapid growth of the smart home market, homeowners now have more options than ever to create intelligent, connected spaces that boost comfort, security, and energy efficiency.
Investing in home automation technology sets up your property future-proof providing immediate benefits in convenience, safety, and energy management, depending on your decision. The key is to pick an architecture that meets your current needs while remaining flexible enough to grow and adapt over time.
Ready to transform your home with smart automation? Keep your needs, budget, and goals in mind while deciding between a central or decentralized system. The perfect smart home setup is that fits your lifestyle today and adapts as your needs change.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is a smart home hub necessary?
Yes. A hub ensures better reliability, local processing, and a single app to manage all devices.
What happens if the internet goes out?
Hub-based systems (Z-Wave/Zigbee) continue core automations. Cloud-dependent Wi-Fi devices may lose remote access until restored.
Which is more reliable, Z-Wave or Zigbee?
Both are reliable. Z-Wave may be more robust due to less congested frequencies, but device availability and cost matter more.
What are the security risks?
Risks include data breaches, hijacking, and network attacks. Use strong passwords, network segmentation, and regular updates to stay secure.
What is the Matter standard?
Matter is a universal protocol enabling devices from different brands to work together, improving compatibility and flexibility.