Have you ever noticed the tiny Bluetooth icon appearing on your phone or smart speaker whenever you connect your devices wirelessly? It is not just a symbol but more than linking your headphones; it’s actually a key to a secret universe of features built into the everyday gadgets we use daily.
In this detailed guide, we’ll uncover some of the overlooked Bluetooth functions in smart devices, showing how this technology can really change how your home works.
Whether you’re adjusting your wireless thermostat or connecting several Bluetooth devices, knowing how to use these features can make your everyday life easier and more connected.
Let’s start this journey by diving into the details. It’s actually a major player in modern living that makes Bluetooth more than just a handy feature.
Imagine this: you’re relaxing on your couch, and with just a voice command, your lights get dimmer, your music starts playing, and your thermostat adjusts to the ideal temperature—all thanks to Bluetooth-enabled smart home devices.
But there’s way more to it than meets the eye.
Many people don’t realize the advanced options Bluetooth has to offer, like increasing its range or linking it with other systems.
As we go deeper, you’ll discover these lesser-known tricks that can take your setup from ordinary to outstanding. And honestly, once you start using them, you’ll think you couldn’t have lived without them before.
- The Evolution of Bluetooth
- Unleashing the Potential: Bluetooth Versions and Their Secret Strengths
- The Heart of Connectivity: Understanding Bluetooth Low Energy
- Advanced Layers: Diving into the Bluetooth Protocol Stack
- Services and Attributes: The Building Blocks of Interaction
- Mesh Networks: Expanding Horizons in Smart Homes
- Smart Thermostats: Where Bluetooth Shines Bright
- Powering Up: Batteries and Efficiency in Bluetooth Ecosystems
- Security and Control: Navigating the Technical Depths
- Integrating with Other Ecosystems: Bluetooth's Versatile Edge
- Real-World Applications: Bringing It All Home
- Overcoming Challenges: Tips for Maximizing Bluetooth Potential
- FAQ
- Conclusion
The Evolution of Bluetooth
Let’s begin with the fundamentals. Bluetooth was created in 1994 when a team at Ericsson had the idea of using wireless technology to replace tangled cables. The first version came out in 1999 which changed the way devices communicate with each other. Now, Bluetooth is everywhere, found in earphones, smart fridges, and many other devices. Knowing this history helps us better understand the advanced features we now use without even thinking about them.
Bluetooth has gone through a lot of changes over the years.
Each new version improves speed, efficiency, and the Bluetooth range. For example, the most recent version offers better data transfer and uses less power. These improvements affect your everyday life—fewer dropped calls, longer battery life, and more stable connections between your gadgets. It’s similar to watching something simple evolve into something much more complex, but in the world of technology. Bluetooth uses the 2.4 GHz frequency band, which is also used by Wi-Fi and microwaves.
Smart engineering allows it to switch between different channels, avoiding interference like a professional athlete dodging tackles. Choosing the right frequency is important because it lets Bluetooth function effectively in small devices without using too much power.
Unleashing the Potential: Bluetooth Versions and Their Secret Strengths
Now, let’s talk versions—because not all Bluetooth is created equal.
- The Bluetooth 5.3 update refined audio streaming and location services, making it a favorite for wearables.
- Bluetooth 5.4 takes it up a notch with better security and periodic advertising, ideal for crowded environments like busy offices or homes packed with gadgets.
- Looking ahead, Bluetooth 6.0 brings even more improvements, such as channel sounding, which allows for accurate distance measurement. Picture your smart lock recognizing when you’re approaching from far away and unlocking the door just as you get there.
These improvements aren’t just eye-catching news, but they quietly make connections more dependable and pave the way for new and useful ideas.
Another thing that’s often overlooked is how far Bluetooth can reach. It typically works between 10 to 100 meters, depending on the surroundings, and this distance can be boosted with smart tricks like using repeaters or positioning antennas better.
In a smart home setup, this means you can control lights from the backyard or check on sensors in distant parts of your house without any trouble.
The Heart of Connectivity: Understanding Bluetooth Low Energy
Bluetooth Low Energy, or BLE, is an important part of many modern technologies. Similar to sipping a glass of wine slowly it uses power very efficiently, allowing devices to work for months on just a single small battery. It works quietly behind the scenes in fitness trackers and beacons, sending small bits of data smoothly without needing to charge often.
This is really helpful because in today’s fast-paced life, having devices that don’t need to be replaced as often gives you a great benefit. For instance, the Nest thermostat uses BLE technology to link with your smartphone, allowing it to change the heating or cooling based on your location. This helps save energy and ensures your home is at a comfortable temperature when you return, without using unnecessary power when you’re not there.
Bluetooth Low Energy works well with other technologies. Take a HomeKit thermostat, for instance—it connects with Apple’s ecosystem, letting you control it with Siri or set up automatic schedules. It’s like having a personal assistant that’s always ready, but in the most convenient way possible.
Advanced Layers: Diving into the Bluetooth Protocol Stack
To really discover the secret abilities of Bluetooth in smart devices, we need to look closely at the Bluetooth protocol stack. This is a layered system that takes care of everything from the physical connection to how data is used in apps. At the very bottom, the physical layer deals with radio signals, while higher layers use profiles to decide how devices talk to each other.
The key components of this system are L2CAP and RFCOMM. L2CAP is responsible for handling multiple data streams, while RFCOMM functions like a regular serial port, making it compatible with older devices. Together, they provide a reliable and consistent connection for communication.
Another essential part is the Bluetooth Host Controller Interface (HCI) control mode.
This connects the main device to the Bluetooth controller. Knowing how to use HCI commands lets developers make exact changes, such as adjusting the device’s power settings or how frequently it looks for connections. It’s a bit technical, but it gives the ability to build custom solutions for specific requirements.
Services and Attributes: The Building Blocks of Interaction
As we move up the stack, the Bluetooth Low Energy Generic Attribute Service, or GATT, plays a key role in Bluetooth low energy systems. GATT structures data into services and characteristics, which makes it simple for devices to access or modify data. For example, a heart rate monitor uses GATT to share its information, so your phone can show live updates on your heart rate.
Closely related is Bluetooth BT GATT, which standardizes how attributes are accessed. This structure ensures interoperability, so your Bluetooth devices from different brands play nice together. It’s the glue holding the ecosystem intact.
In practice, the Bluetooth GATT service enables scenarios like remote health monitoring or automated home adjustments. Imagine your fitness watch sending a signal to your thermostat to turn on the AC after a tough workout, just made possible by these protocols.
Understanding the Bluetooth Protocol Stack Diagram
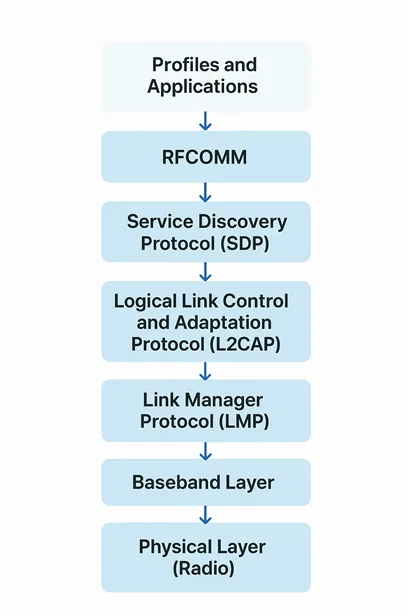
The Bluetooth protocol stack diagram shows the layered structure that allows devices to communicate wirelessly over short distances creating personal area networks (PANs). It is usually drawn as a vertical stack, similar to the OSI model, but designed specifically for Bluetooth’s ability to work efficiently with low power and temporary connections.At the base lies the Radio Layer (Physical Layer), handling signal transmission in the 2.4 GHz ISM band using frequency hopping to avoid interference. Above it, the Baseband Layer manages packet formats, timing, and links like synchronous (SCO) for audio or asynchronous (ACL) for data.
Next, the Link Manager Protocol (LMP) oversees link setup, security, authentication, and encryption. The Host Controller Interface (HCI) acts as a bridge between hardware (controller) and software (host), standardizing commands for interoperability. Higher up, the Logical Link Control and Adaptation Protocol (L2CAP) adapts upper-layer data to baseband formats, supporting connection-oriented and connectionless services. The Service Discovery Protocol (SDP) enables devices to query services for connections.
The diagram is usually divided into several partsFor Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), the Controller, which includes the PHY and Link Layer, is followed by the HCI, then the Host layer that contains GAP for roles like Central and Peripheral, and finally the Application layer. This setup focuses on making the technology more energy-efficient. The diagrams use arrows to show how data travels between these layers. They also include separate sections for widely accepted standard key protocols, like TCP/IP, and newer protocols that replace physical cables, such as RFCOMM. This way of presenting the structure highlights Bluetooth’s flexibility, allowing devices to use only the parts they need. This makes it ideal for use in IoT devices and smart gadgets. The diagram helps break down complicated processes, making it easier for developers to build reliable systems.
| Layer | Stack Segment | Key Function |
| Profiles and Applications | Host (Top) | Define vertical standards for specific use cases (e.g., audio streaming, data sync). Examples: GATT (Generic Attribute Profile for BLE), A2DP, HFP. |
| RFCOMM | Host | Emulates a serial port (RS-232) to support legacy and simple data stream applications. Built over L2CAP. |
| Service Discovery Protocol (SDP) | Host | Allows a device to query and find services available on a remote Bluetooth device. Built over L2CAP. |
| Logical Link Control and Adaptation Protocol (L2CAP) | Host | Provides data multiplexing (allows multiple upper layers to share one Baseband link), packet segmentation, and reassembly. The foundation for all Host protocols. |
| Host Controller Interface (HCI) | Interface | Provides a standardized command and data interface between the Host (software/OS) and the Controller (hardware chip). |
| Link Manager Protocol (LMP) | Controller | Responsible for link setup, link authentication, encryption (security), and controlling the power modes of the link (e.g., sniff, hold). |
| Baseband Layer | Controller | Handles the physical link establishment, frequency hopping, packet framing, timing, and connection management. |
| Physical Layer (Radio) | Controller (Bottom) | The lowest layer, responsible for the actual wireless transmission and reception of raw bits over the 2.4 GHz Industrial, Scientific, and Medical (ISM) radio band. |
Mesh Networks: Expanding Horizons in Smart Homes
The Bluetooth mesh network is one of the coolest hidden features. A Mesh Network creates a hidden network unlike the usual direct connections between devices, forming a solid network that can cover bigger areas. This is a big upgrade for smart homes, where signals sometimes struggle to get through walls or over long distances.
In a Bluetooth mesh network, each device acts as both a sender and a receiver, meaning there’s no single weak point that can cause the whole system to fail.
It’s resilient, like a team where everyone backs each other up. For Bluetooth range in smart home setups, this means controlling basement lights from upstairs without extenders.
Comparing protocols, Bluetooth vs Zigbee often comes up. Bluetooth works well with a wide range of devices and connects easily with smartphones, whereas Zigbee is better for low-energy mesh networks that work with sensors. Neither one is better than the other—it all comes down to what the user needs. Bluetooth is chosen for its flexibility, while Zigbee is preferred for specific network setups.
Smart Thermostats: Where Bluetooth Shines Bright
Let’s zoom in on thermostats, a prime example of Bluetooth smart home devices. A smart thermostat with Bluetooth, like the Nest or Ecobee, uses Bluetooth to pair with apps, enabling precise control and energy savings. The Nest thermostat stands out with its learning algorithms, adapting to your schedule over time.
But how does it stack up in Ecobee vs Nest? Ecobee often wins with its thermostat with remote sensor, placing sensors in multiple rooms for even heating. Nest, however, integrates seamlessly with Google Assistant, making it ideal for voice-centric homes.
Don’t overlook the Tuya smart device ecosystem, which leverages Bluetooth for affordable, app-controlled thermostats. These devices make smart living accessible to everyone, showing that you don’t need a lot of money to enjoy powerful features.
For Apple users, a HomeKit thermostat adds Bluetooth support, letting you control it securely and locally without relying on the cloud. It also prioritizes privacy, keeping your data safe and on your device.
Powering Up: Batteries and Efficiency in Bluetooth Ecosystems
Battery life is very important, especially for gadgets you take with you. The Nest thermostat shows how Bluetooth Low Energy helps preserve battery power, letting the device last for weeks without needing a charge. Smart sleep modes keep the device inactive when not in use and only send data when necessary.
Bluetooth devices, in general, are designed to use very little power while still performing their tasks effectively.
Adaptive frequency hopping is a method that helps cut down on interference, which in turn makes the device work longer. It’s a careful process, but ultimately it leads to improved and more dependable performance.
Security and Control: Navigating the Technical Depths
Security is very important in today’s digital world; however, it might not look exciting. The Bluetooth protocol has different layers that help with encryption, which keeps your communications safe from people listening in. Knowing about Bluetooth HCI commands can help when checking for weaknesses in your system, making sure everything is secure.
For those who want to go deeper, looking into BT HCI control mode gives you the chance to tweak security settings.
It’s as if you have the keys to your digital life, letting you take more control and gain greater power.
Integrating with Other Ecosystems: Bluetooth’s Versatile Edge
Bluetooth doesn’t exist in isolation. In smart home battles like Bluetooth vs Zigbee, Bluetooth often complements rather than competes. Hybrid systems combine both technologies for the best coverage—Zigbee is great for handling many sensors in a tight area, while Bluetooth works well for connecting devices directly.
When setting up a smart home, considering Bluetooth range is key. By positioning the devices properly and using a mesh network, you can maximize their performance. It really comes down to smart planning, and you can turn any limitations into good results.
Real-World Applications: Bringing It All Home
In daily life, these abilities show up in small but meaningful ways. For example, your wireless thermostat can adjust the temperature based on whether someone is in the room, detected through Bluetooth beacons. Similarly, a smart thermostat with Bluetooth can connect to weather apps and prepare for changes in temperature before they happen. Companies like Ecobee and Nest showcase this feature, with Ecobee offering remote sensors that give detailed control. This isn’t just about making things easier—it’s also about saving money and helping the environment through better energy use.
Overcoming Challenges: Tips for Maximizing Bluetooth Potential
Of course, no technology is completely flawless. Bluetooth can sometimes experience interference, but there are ways to deal with it, such as blocking certain channels. For a better range, you can lift the devices higher or use amplifiers carefully.
When it comes to Bluetooth smart home devices, making sure they are compatible is essential. Always go for certified products to avoid problems. Also, keep your firmware up to date—new versions, like Bluetooth 5.4, often fix issues and add new features.
FAQ
Conclusion
As we look ahead, Bluetooth 6.0 is coming soon, offering the potential for highly precise positioning and better sound quality. Imagine augmented reality glasses that use Bluetooth to deliver truly engaging experiences, or health trackers that provide real-time updates on your vital signs.
This progress brings us back to the main idea: discovering the extra capabilities of Bluetooth in smart devices can help make your home ready for the future.
It’s an exciting time, with innovations just on the horizon.
To wrap things up, we’ve explored the journey of Bluetooth, from its beginnings to its latest uses.
By using these less commonly known features, you can create a smarter and more engaging environment. Whether you’re adjusting your Bluetooth settings or connecting a smart thermostat to your home network, there are countless options available. Take advantage of these possibilities and see how your smart devices go beyond being simple tools—they can become true parts of your everyday life.
If you’re eager to elevate your space and experience these hidden powers firsthand, why not explore the Ecobee Smart Thermostat Premium today and start reaping the rewards— your cozy, cost-effective haven awaits


