The magic behind your smart home automation isn’t just in the devices themselves—it’s in how they talk to each other.
When your motion sensor triggers the hallway lights, or your smart thermostat adjusts based on your phone’s location, there’s an invisible conversation happening. Understanding how devices communicate in home automation can transform your approach to building a truly connected home.
Modern smart homes rely on sophisticated communication protocols that act as digital languages, allowing devices from different manufacturers to work together seamlessly. These protocols have evolved dramatically, especially with the introduction of the Matter protocol in 2024, which promises to unify the fragmented smart home ecosystem.
- What Are Home Automation Communication Protocols?
- The Major Players: Key Home Automation Protocols
- How Mesh Networks Transform Home Automation
- Device Discovery and Pairing Processes
- Network Topology Types in Smart Homes
- Device Communication Security
- Troubleshooting Common Communication Issues
- Smart Home Security Key Considerations
- Future Trends in Home Automation Communication
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Building Your Connected Future
What Are Home Automation Communication Protocols?
Think of communication protocols as the languages your smart devices use to share information. Just like humans, your smart thermostat, lighting system, and security cameras need agreed-upon rules for exchanging data and a common language to communicate effectively.
A device used to communicate with other devices, a smart home protocol is the language or the main controller, enabling everything from simple on/off commands to complex automation sequences.
These protocols shape how well devices perform within your home:
- Range and coverage determine whether your smart doorbell can prompt your living room lights to turn on.
- Power consumption and battery life decide if a sensor lasts months or drains in days.
- Data transmission speed and reliability influence whether commands respond instantly or lag.
- Security encryption levels ensure your system resists tampering.
- Device compatibility across brands affects whether your voice assistant can control various smart blinds.
The choice of protocol affects whether your smart doorbell can trigger your living room lights or if your voice assistant can control your smart blinds.
The Major Players: Key Home Automation Protocols
Wi-Fi: The Household Champion
Wi-Fi remains the most familiar and convenient protocol for engaging in home automation. There’s no need for additional hubs or bridgesWith an existing router already in place, connect, configure, and go.
Advantages:
- High-speed data transmission
- Direct internet connectivity
- Wide device compatibility
- Easy setup process
Drawbacks:
- Higher power consumption
- Network congestion with many devices
- Limited range without extenders
- Security vulnerabilities exist if not properly configured
Real-world example: Your smart security cameras likely use Wi-Fi to stream high-definition video to your phone, requiring the bandwidth and internet access that Wi-Fi provides.
Zigbee: The Mesh Networking Pioneer
Zigbee protocol operates on the 2.4GHz frequency but uses significantly less power than Wi-Fi. Mesh topology comes with just one coordinator alongside several end devices and routers, creating a self-healing network.
This mesh network topology means each device can act as a repeater, extending the network’s reach throughout your home. The network automatically routes around it if one device fails.
Key benefits:
- The battery life for some devices has been extended to years
- Self-healing mesh capability
- Support for hundreds of devices
- Strong security with AES-128 encryption
Practical application: Your smart light switches using Zigbee can relay signals to devices in distant rooms, creating a robust network that grows stronger with each added device.
Z-Wave: The Reliability Expert
The crowded 2.4GHz band is completely avoided by Z-Wave technology, which operates on sub-1GHz frequencies. The dedicated frequency offers exceptional reliability and range.
Z-Wave is the perfect choice for complete control over critical systems like locks and alarms, and it is compatible with many home security systems.
Z-Wave advantages:
- The use of a dedicated frequency reduces interference
- The range is exceptional (up to 100 meters outdoors)
- The use of a strict certification process ensures compatibility
- Military-grade security
In reality, Z-Wave’s reliability benefits your smart door locks and security sensors. It’s important to prevent these crucial devices from losing connection.

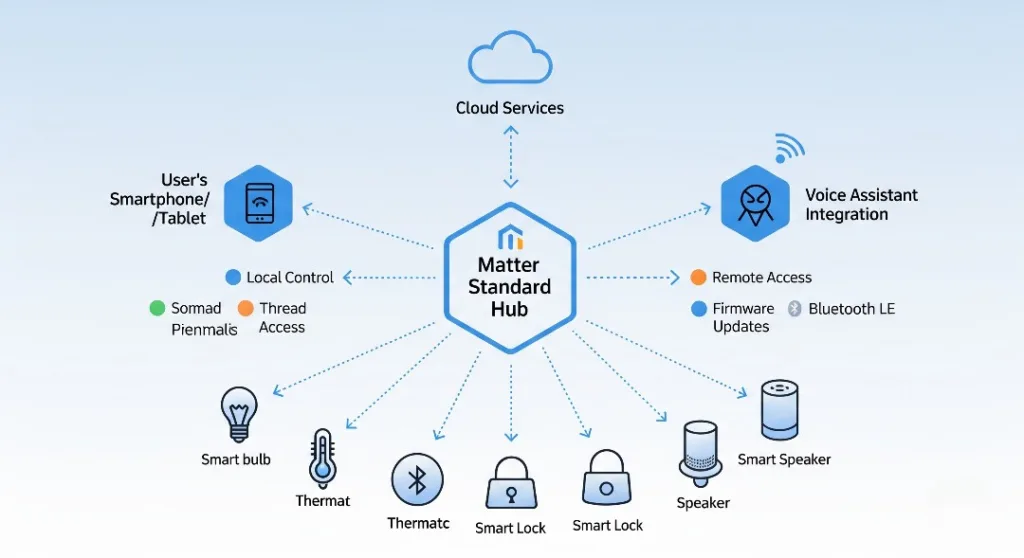
Thread and Matter: The Future is Here
Matter is a new protocol that will become highly popular in 2024. The Connectivity Standards Alliance (CSA) developed Matter to bring unity to the smart home ecosystem by offering a single, secure, and reliable protocol for devices from different manufacturers.
Thread is responsible for networking, while Matter is responsible for the application layer and device interoperability across brands.
Revolutionary features:
- There is no need for proprietary hubs
- Connects to Apple HomeKit, Google Home, and Amazon Alexa simultaneously
- Future-proofing requires IPv6-based connectivity.
- End-to-end encryption
Bluetooth and Proprietary Solutions
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) excels for personal devices and proximity-based automation. Meanwhile, some manufacturers still prefer proprietary protocols for specialized applications.
BLE mesh introduced a new topology for BLE: many-to-many. This is generally referred to as mesh topology, where many mesh devices can communicate with many other mesh devices within the same network using mesh nodes.
How Mesh Networks Transform Home Automation
Understanding mesh network topology is crucial for modern smart homes. Mesh Topology is a network configuration where every device is interconnected with every other device, providing multiple routes for data to travel.
The Power of Redundancy
Traditional star networks create single points of failure—if your central hub fails, everything stops working. By creating multiple pathways for data mesh networks eliminate this vulnerability.
Mesh advantages:
- Automatic rerouting around failed devices is a self-healing capability
- Each device has an extended range and acts as a signal repeater
- Multiple paths prevent communication failures, resulting in improved reliability
- Scalability is achieved by adding devices without requiring infrastructure changes.
Real-World Mesh Implementation
Imagine your smart home as a neighbourhood where everyone knows everyone else. When you dim the kitchen lights using your smartphone:
- Your phone sends the command to the nearest mesh device
- That device passes it along the most efficient path
- Multiple devices relay the signal simultaneously
- The kitchen light switch receives and executes the command
- Confirmation travels back through the mesh to your phone
This happens in milliseconds, creating the seamless experience you expect.
Device Discovery and Pairing Processes
Device discovery in home automation involves several sophisticated mechanisms that work behind the scenes to create seamless connectivity.
Automatic Network Discovery
In modern smart home devices, broadcast protocols are used to announce their presence. A new smart outlet immediately advertises its capabilities to nearby devices and hubs upon plugging in.
The discovery process usually involves:
- Scanning the network for available connections
- Negotiating capabilities between devices
- Encrypted key exchange is used for a security handshake
- Achieving network integration with assigned addresses
Hub-Based vs. Hubless Systems
Smart home hubs make it easier to manage all your devices and help them talk to each other. With a single hub, you can connect devices that use different communication methods like Zigbee, Z-Wave, and Wi-Fi. This hub acts like a translator so all the devices can work together smoothly.
Some systems don’t use a hub at all.
Instead, hubless systems rely on the cloud and let devices communicate directly with each other. Thread is an IoT protocol, but it’s not a mesh network like Zigbee or Z-Wave. It doesn’t need a hub, which means there’s no single point that could fail.
Network Topology Types in Smart Homes
Star Topology: The Traditional Approach
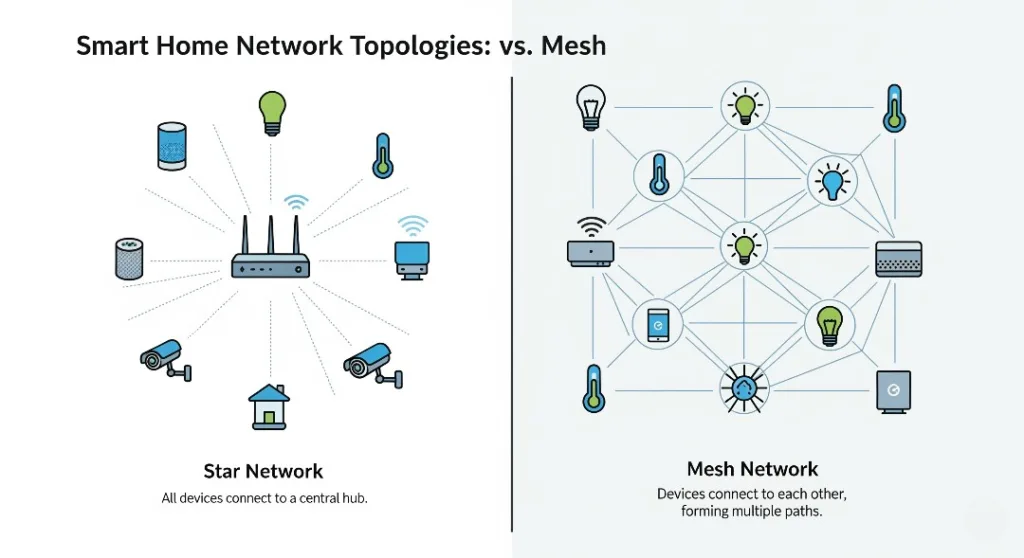
The central hub is connected with each device using star topology. It is a well structured and common approach to manage all devices. If the hub fails whole system goes down.
Benefits:
- Centralized control and monitoring
- Easy to troubleshoot
- Consistent performance and management
Limitations:
- Hub failure turns off the entire network
- Limited by the hub’s processing capacity
- Range restricted by the central point
Mesh Topology: The Modern Standard
Mesh topology describes a network structure where devices—or nodes—are interconnected, with each node linked to one or more others. In a fully connected mesh, every node maintains a direct connection to every other node, making the network exceptionally resilient and fault-tolerant.
In a partial mesh configuration, devices are connected to multiple peers—but not all—offering robust connectivity without the complexity of linking every device to every other one.
Hybrid Approaches: Best of Both Worlds
Many modern smart homes combine multiple topologies. Wi-Fi devices connect directly to your router in a star setup, while Zigbee devices interlink through mesh.
Device Communication Security
Device communication has a big impact on smart home security system and their protocols.
Encryption Standards
Modern protocols implement robust security measures:
- Zigbee uses AES-128 encryption for communications
- Wi-Fi uses WPA3 security for connections
- End-to-end encryption in Matter/Thread networks
- Rolling codes for critical devices like garage door openers
Network Segmentation
A common best practice is to set up smart home devices on their own separate network, away from your regular devices. This helps ensure that if one part of the network is affected, it doesn’t spread to the rest of your network.
Regular Security Updates
Ensure your smart home devices and platforms receive regular firmware updates. Even though Matter devices using different protocols function well due to their ability to communicate interactively and get frequent security updates.
Troubleshooting Common Communication Issues
Smart homes rely on wireless communication—but signals aren’t always perfect. Issues like interference, limited range, or too many devices competing for bandwidth can disrupt performance. Here’s how to spot the problems and fix them.
Signal Interference
Wireless signals can get blocked by common items and structures found around your home. Some typical causes of interference are:
- Microwave ovens, especially those operating at 2.4GHz
- Baby monitors and cordless phones
- Other nearby Wi-Fi networks
- Metal objects, walls, and big furniture items.
Solutions:
- For a cleaner channel switch to 5GHz Wi-Fi whenever possible
- Place mesh repeaters in strategic locations to boost coverage
- Use devices that run on different frequencies to avoid clashes
- Position antennas properly to strengthen signal reception
Range Limitations
Each type of wireless protocol has different strengths and weaknesses when it comes to coverage. Knowing these can help you place your devices better:
- Wi-Fi can reach up to 150 feet inside a house, but walls can weaken the signal.
- Zigbee works up to 30–60 feet with each connection, and it can go further if you use a mesh network.
- Z-Wave can cover up to 330 feet in open space.
- Bluetooth is reliable within about 30 feet.
The main point is to pick the right protocol for your home setup and use mesh networks when needed to improve coverage.
Network Congestion
As your smart home grows, more devices fight for the same bandwidth. This can lead to laggy responses, delays, or dropped connections.
Strategies to reduce congestion:
- Spread devices across different networks rather than relying on just one.
- Use mesh-based protocols that automatically manage and balance the network load.
- Set up Quality of Service (QoS) to give priority to important devices such as security cameras or alarm systems.
- Keep checking and improving your network regularly to ensure it works well and stays efficient.
Smart Home Security Key Considerations
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Device Communication Security | The communication protocols and system setup methods have a major impact on overall smart home security. |
| Encryption Standards |
|
| Network Segmentation | Place smart home devices on a separate network segment from everyday internet devices; if one segment is compromised, it will not cascade across the rest. |
| Regular Security Updates | Ensure devices and platforms receive frequent firmware updates. Matter helps keep multi-protocol ecosystems compatible and secure through coordinated update mechanisms. |
Future Trends in Home Automation Communication
The Matter Revolution
Popular protocols such as Zigbee, Thread, Matter, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth each have their own advantages, but combining them can create confusion. Purchasing devices without verifying if they work together can result in wasted time and money. The Matter protocol helps solve this issue by ensuring devices can connect and work smoothly across different platforms and brands.
Edge Computing Integration
Edge computing brings the power to process information closer to the devices, which helps reduce delays and enhances privacy. When processing happens locally, your voice commands and automation settings can work even without an internet connection.
AI-Powered Optimization
Machine learning algorithms are becoming better at improving network performance by:
- forecasting how much data will be used,
- changing the best paths for data to travel on its own,
- spotting and fixing problems,
- and making sure the network uses less energy.
Enhanced Security Measures
Future improvements will include:
- Quantum-resistant encryption protects data even against future quantum computing threats.
- Blockchain-based device authentication, which uses blockchain technology to securely verify the identity of devices.
- Zero-trust network architectures, which assume no device is trustworthy and require continuous verification.
- Biometric device pairing, which uses unique biological traits to connect and authenticate devices.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the best communication protocol for home automation?
There is no single best option—it depends on your needs. Wi-Fi works well for cameras, while Zigbee and Z-Wave are great for sensors and lighting. Thread and Matter are promising for future-proofing.
Do all smart devices need the internet to work?
No. Many devices can operate locally without internet, especially those using Zigbee, Z-Wave, or Thread. However, cloud-based control is needed for remote access.
Can devices using different protocols work together?
Yes, with the help of a smart hub or platforms like Alexa, Google Home, or Apple HomeKit, different protocols can interconnect.
Is Matter going to replace Zigbee and Z-Wave?
Matter won’t necessarily replace them but will create a universal compatibility layer, making it easier for devices using different protocols to work together.
Building Your Connected Future
Understanding how devices talk to each other in a smart home setup helps you make smarter choices when it comes to investing in your home automation system. The communication method you pick now can have a big impact on how easily you can add more devices, how dependable your system is, and how safe your home remains over time.
The move toward the Matter protocol and mesh networks is more than just a tech upgrade—it’s the key to building really smart homes that can adjust, learn, and react to what your family needs.
Whether you’re starting with just one smart light or planning a full automation system, remember that the most successful smart homes focus on having strong, dependable communication rather than just having lots of cool features.
Pick protocols that fit your long-term plans, and feel free to combine different solutions to get the best results.
Ready to create a smart home that works smoothly?
Look for existing network setups and determine which communication methods work best for your automation goals. Starting with choosing the right protocol, your ideal connected home is just a few steps away.


